The Pad foundations are a type of shallow foundation made of reinforced Concrete. Pad Foundations are simple, cost-effective, and typically used for light to moderate loads in stable soil conditions near the surface. Still, they are not suitable for unstable ground or heavy loads.
Recommended Articles
- How To Design a Combined Footing in Accordance with BS 8110
- Design of Staircase: The Complete Guide to Civil Engineers
- Substructure and Superstructure: The Complete Guide
- What is a Lateral Forces: The Complete Guide
- Everything You Need To Know About The Transmission of Water
- Cracks In The Building: The Complete Tips for Engineers
Table of Contents
Design of a Pad Foundation
Please note: This design is based on BS 6399 Part 1:1984 Code of Practice of Dead Load and Imposed Load, BS 8110 Part 1:1985 Code of Practice for design and Construction, and BS 8110 Part 1: 1997 Code of Practice for design and Construction.
Let’s start with making assumptions:
- Ultimate designed axial load = 2014.1KN
- Serviceability axial load = 1438.64KN
- Serviceability moment = 16.81kNm
- Fcu = 30N/mm2
- Fy = 460N/mm2
- Soil bearing capacity = 200kN/m2
For the serviceability limit state
- Assumed footing weight = 120KN
- Total serviceability load = 1438.64 + 120 = 1558.64KN

Therefore, from above:
- P = N/BD + 6M/BD2
- Where P is the safe bearing capacity
- Assume square footing, i.e., B = D
- P = N/B2 + 6M/B3 = 1558.64/ B2 + 100.86/ B3
Therefore:
- 200 kN/mm2 = 1558.64/ B2 + 100.86/ B3
- Solve for B, which will be equal to 2.8m
- Provide a base 2.8 m square, area = 7.8m2
Eccentricity, e:
- Eccentricity, e = M/N = 16.81 kNm/1558.64kN
- e = 0.01m
- D/6 = 2.8/6 = 0.47
- Therefore, e = 0.01m < D/6 = 0.47
For the ultimate limit state
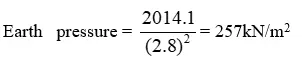
Assume a 625mm thick footing, and with the footing constructed on a blinding layer of Concrete, the minimum cover is taken as 50mm.
Therefore:
- self-weight of footing = Area * h * γconcrete
- 7.8 * 0.625 * 24 = 117KN < assumed weight, 120KN
Bending Reinforcements
At the column, which is the critical section
- M = earth pressure * pad size * (projection/2)2

From above;
- Provide: Y25 – at 125mm centres
- As prov = 3927mm2
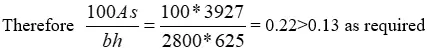
Maximum spacing = 750mm. Therefore, the Reinforcement provided meets the requirements specified by the code for minimum and maximum bar spacing in a slab.

- Provide: Y25 – at 200mm centres
- As prov = 2454mm2
Punching shear
- Critical perimeter = column perimeter + 8 *1.5d
- Critical perimeter = 4 * 300 + 12 * 565= 7980mm
- Area within perimeter = (300 + 3d)2 = (300 + 3 * 565)2
- Area within perimeter = 3.98 * 106
Therefore:
- Punching shear force, V = 257kN/m2 (7.8m2 – 3.98m2)V = 982KN
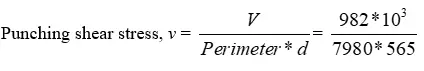
- Punching shear stress, v = 0.22N/mm2
- From table 3.9 BS 8110 -1- 1985, vc = 0.4N/mm2
Therefore:
- Modified vc = [30/25]⅓ * 0.4 = 0.43 N/mm2
- 0.5vc < v < (vc + 0.4)
- 0.5*0.43 < 0.22 < (0.43 + 0.4) 0.215 < 0.22 < 0.83 OK
Shear stress
At the critical section for shear, 1.0d from the column face
- V= 257kN/m2 * 2.8 * 0.625 = 449.75kN
- V = V/bd = 449.75 * 103/2800*565 = 0.28 N/mm2
- 0.28 N/mm2 < 0.43 N/mm2
Therefore, the section is adequate in shear.
FAQs on Pad Foundation
1. What is a Creep?
Creep is the continuous deformation of a material or member under a sustained load.
2. Which conditions influence the durability of Concrete?
The durability of the Concrete can be influenced by:
(1) the exposure conditions
(2) the Concrete quality
(3) the cover to the Reinforcement
(4) the width of any cracks.
3. What are the most crucial serviceability limit states?
Generally, the most crucial serviceability limit states are:
(1) Deflection
(2) Cracking
(3) Durability
4. What types of loads are considered on the structure?
Types of loads to be considered are Dead loads and Live (or imposed) loads.
5. Differentiate dead load from live loads.
Dead loads are those that are generally permanent and constant during the structure’s life, and live loads are transient and are variable in magnitude, for example, those due to wind or human occupants.
6. Why is it necessary to provide laps in Reinforcement?
Lapping of Reinforcement is often necessary to transfer the forces from one bar to another.
Conclusion on Pad Foundation
As defined above, the Pad foundations are a type of shallow foundation made of reinforced Concrete. Pad Foundations are simple, cost-effective, and typically used for light to moderate loads in stable soil conditions near the surface. Still, they are not suitable for unstable ground or heavy loads.
Today, we designed a pad foundation in Accordance with BS 8110. I know you will have learned something, and you need to learn and read more because this profession of structures is broader than what you learned today.
Join the conversation by replying on Bluesky.
That’s all.
If you liked this article, please join Website For Engineers on Twitter, Facebook, TrueSocial, Pinterest, BlueSky, and in our WhatsApp channels.

